Compared with molybdenum disulfide technical grade and Molybdenum disulfide technical fine grade, Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade has incomparable advantages in industrial applications. Molybdenum disulfide itself has good lubricating properties. However, Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade has high temperature, low temperature, high load, high speed, chemical corrosion and modern ultra-high temperature. Under vacuum conditions, Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade has more excellent lubricity for equipment.
Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade is a good solid lubricant that can be lubricated in a vacuum or air environment for a long time. The friction coefficient is relatively low, and Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade can be lubricated for a long time in the air below 350 ℃.
With more than ten years of research and development/ R&D experience, we can provide an annual output of 1,000 tons of Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade as a patented technology product.
Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade
Introduction

Compared with molybdenum disulfide technical grade and Molybdenum disulfide technical fine grade, Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade has incomparable advantages in industrial applications. Molybdenum disulfide itself has good lubricating properties. However, Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade has high temperature, low temperature, high load, high speed, chemical corrosion and modern ultra-high temperature. Under vacuum conditions, Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade has more excellent lubricity for equipment.
Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade is a good solid lubricant that can be lubricated in a vacuum or air environment for a long time. The friction coefficient is relatively low, and Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade can be lubricated for a long time in the air below 350 ℃.
With more than ten years of research and development/ R&D experience, we can provide an annual output of 1,000 tons of Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade as a patented technology product.
Typical MoS2 content (calculated average) is 99.0% (MoS2≥99.0%, HG/T3929-2007 high-purity molybdenum disulfide) .
Chemical Specifications of Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade:
Maximum % by wt | |
Acid Insoluble | 0.50 |
Iron | 0.25 |
Molybdenum Trioxide | 0.15 |
Water | 0.20 |
Oil | 0.40 |
Carbon | 0.50 |
Acid Number | 3.0 |
*Acid number is determined at time of production. Prolonged storage will result in slight oxidation,which will produce an increase in acid number.The smaller particle size grades are more susceptible to surface oxidation.Acid number is expressed as an absolute value and is the mg of KOH required to neutralize the acid in a one-gram sample.
Particle Size Specifications of Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade By Microtrac:
Grade | D50 | D99(Maximum) |
Super Fine | 0.9-1.5μm | 6.5μm |
Typical Particle Size of Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade By Microtrac By Fisher Sub-sizer and Bulk Density:
Grade | Fisher Number, μm | Bulk Density(Scott) |
Super Fine | 0.40 to 0.45 | 0.3g/cm3 |
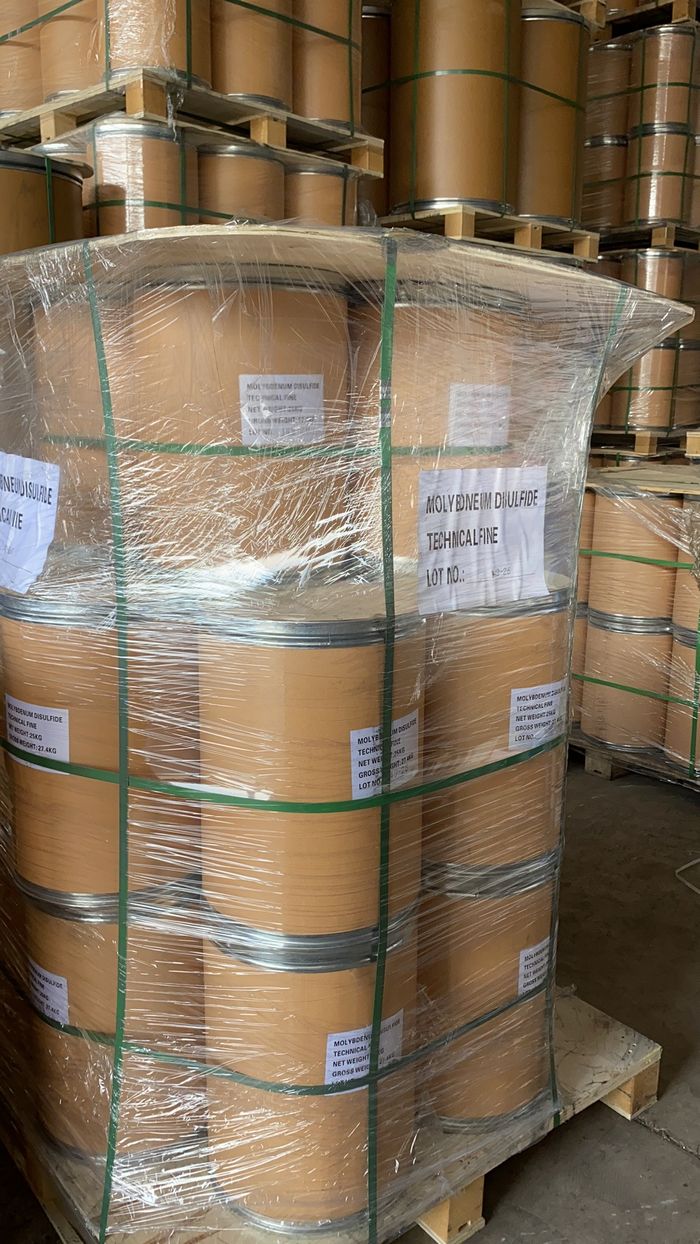
Packaging of Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade :
Grade | US Packaging Fiber Drum | Pallet weight |
Super Fine | 25kg | 450kg |
18 drums/pallet | ||
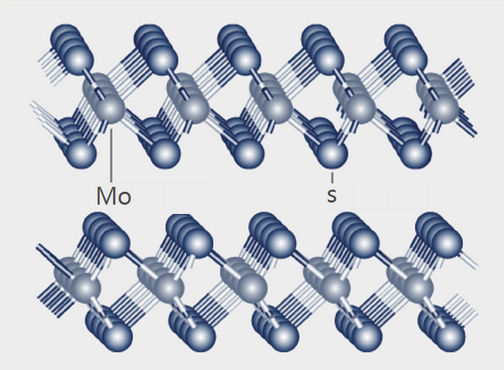
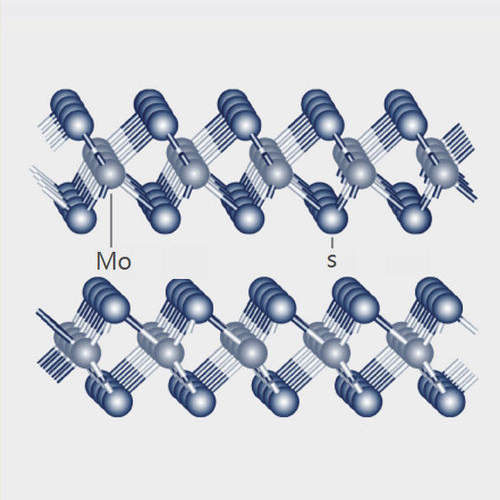
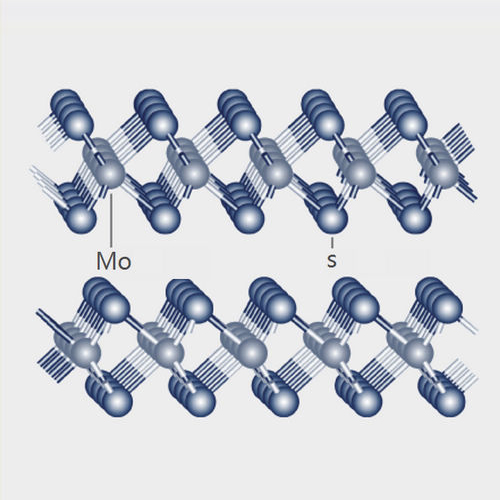
Figure 1: Crystal structure of Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade
The ability of Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade to act as a lubricant is closely related to its layered structure.
The image above shows the layered structure of Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade .The light-colored spheres represent molybdenum atoms, and the dark-colored spheres represent sulfur atoms. An outer layer of sulfur atoms binds to each metal surface, preventing contact between the metal surfaces.
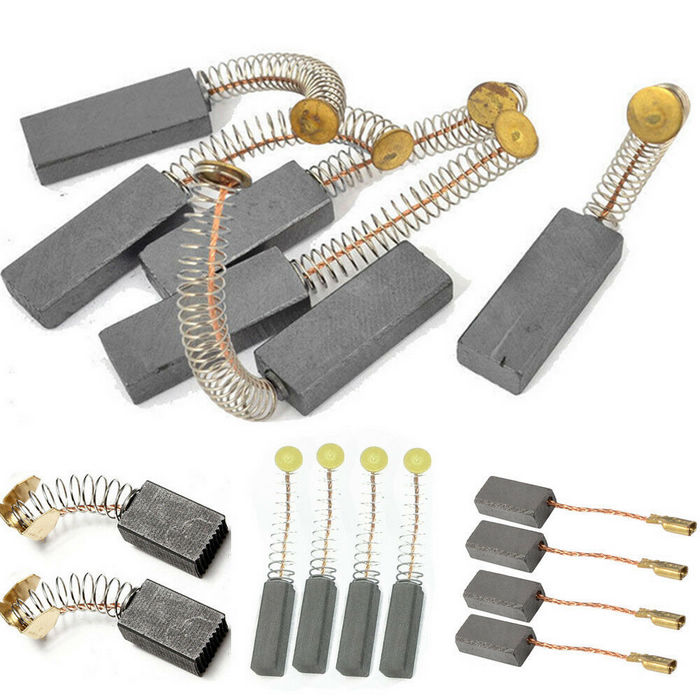

Figure 2: Carbon brushes containing Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade
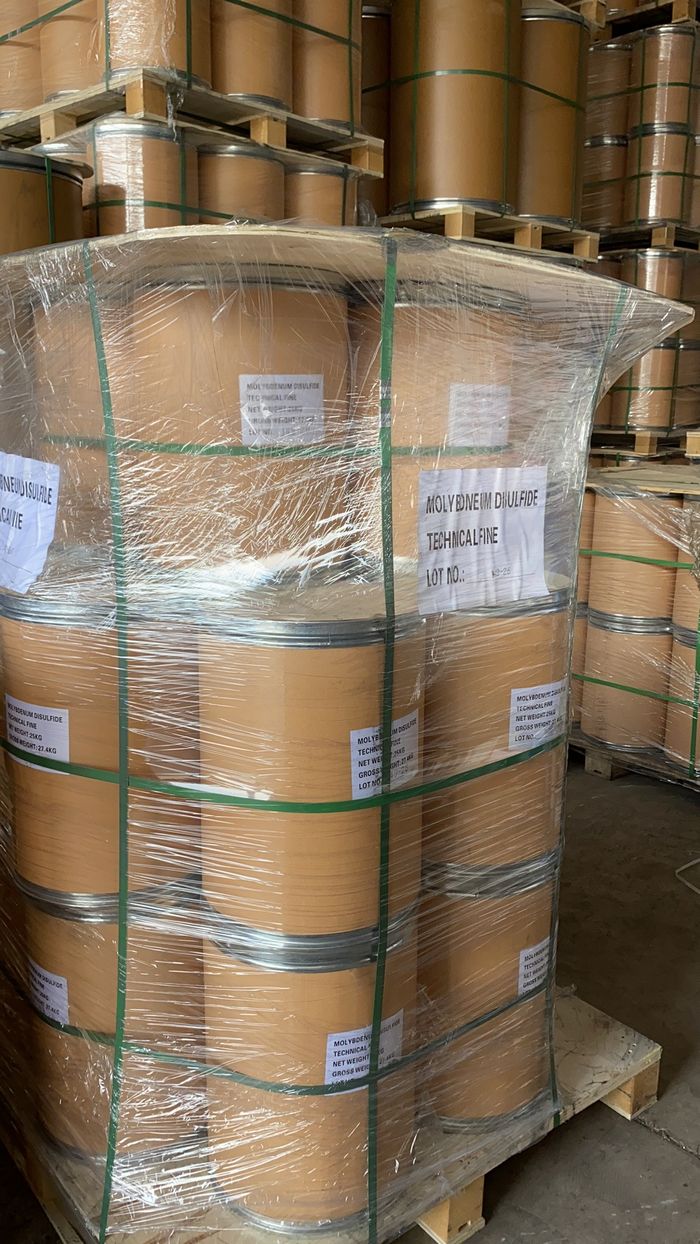

Figure 3: Packaging of Molybdenum Disulfide Superfine Grade
On January 30, 2023, molybdenum price rose by more than 20% in a single day, breaking a new 17-year high. Molybdenum is known as the "war metal", "steel warrior". Molybdenum is valued by more and more countries. China is the world's richest country in molybdenum resources, with reserves of 4.3 million tons, followed by the United States (2.7 million tons) and Chile (1.8 million tons), which acco...more